The Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC)
 was established in 1981 in Abu Dhabi. The original union included the 6 Gulf states of Bahrain, Kuwait, Oman, Qatar, Saudi Arabia and the United Arab Emirates. The main objective was the formulation of similar regulations in various fields such as religion, finance, agriculture, trade, customs, tourism, legislation, administration and transport network. A long-discussed objective is the establishment of a common currency. The GCC has institutionalized forms of cooperation with EU nations. The goal of the GCC is to create opportunities for a trade exchange and support of stable growth in the Gulf region. Alliance treaties, trade treaties, investments and promotion of culture have allowed GCC countries to diverse their economy and become independent from crude oil.
was established in 1981 in Abu Dhabi. The original union included the 6 Gulf states of Bahrain, Kuwait, Oman, Qatar, Saudi Arabia and the United Arab Emirates. The main objective was the formulation of similar regulations in various fields such as religion, finance, agriculture, trade, customs, tourism, legislation, administration and transport network. A long-discussed objective is the establishment of a common currency. The GCC has institutionalized forms of cooperation with EU nations. The goal of the GCC is to create opportunities for a trade exchange and support of stable growth in the Gulf region. Alliance treaties, trade treaties, investments and promotion of culture have allowed GCC countries to diverse their economy and become independent from crude oil.
GCC countries play a major role in North Africa and the Middle East (MENA). During recent decade, countries in those regions reached unprecedented economic growth. In almost all statistics relating to MENA, GCC countries are in the lead, reaching the highest GDP per capita and the lowest rate of unemployment. Liberal politics, the flow of the capital, a free-flowing workforce and actions aimed at limiting foreign debt and increasing investment in infrastructure have helped in achieving such positive results.
Population of the Gulf region (*):
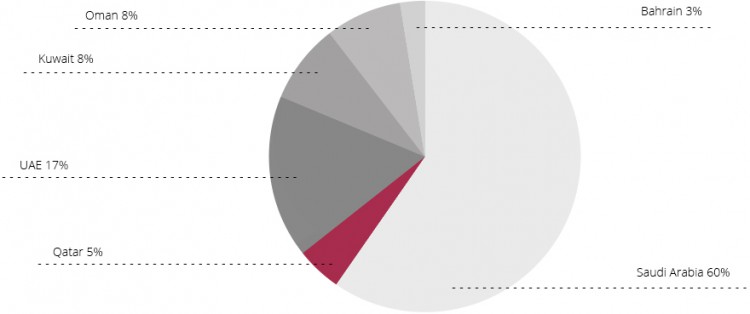
Source: Economist Intelligence Unit, IMF.
(*) EIU: ZEA: 8,4 mln; Saudi Arabia: 29,8 mln; Qatar: 2,3 mln; Kuawait: 4,1 mln; Oman: 3,96; Bahrain: 1,3 mln.
CIA, Fact Book: UAE: 5,6 mln; Saudi Arabia: 27,3mln; Qatar: 2,1 mln; Kuwait: 2,7 mln; Oman: 3,2 mln; Bahrain: 1,3 mln
GDP growth in GCC countries – comparison of the years 2010-2014.
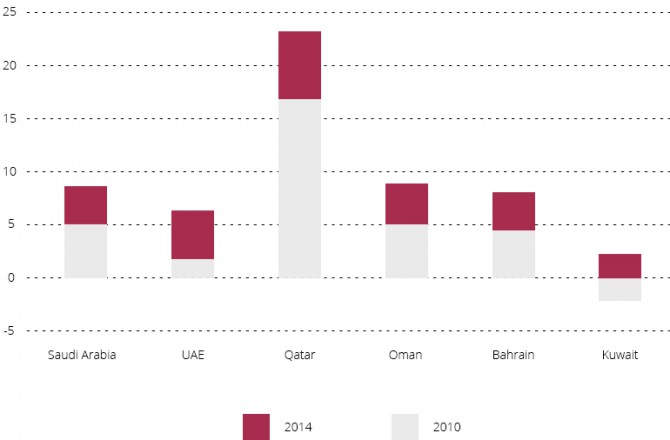
Source: Economist Intelligence Unit, IMF, International Financial Statistics.
GDP per capita in individual countries GCC (in USD)
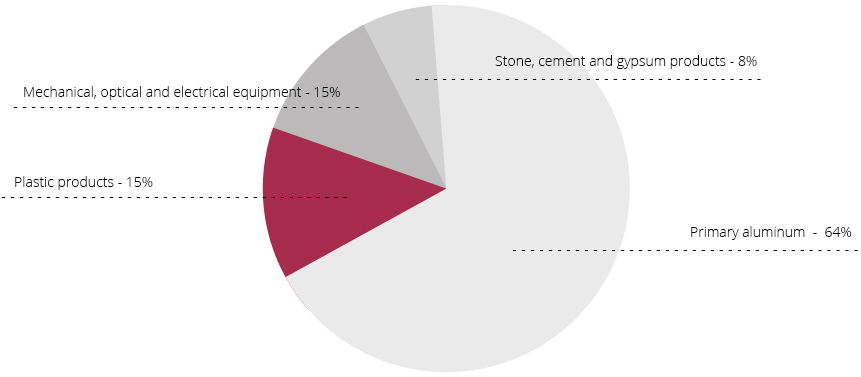
Source: Economist Intelligence Unit, IMF, International Financial Statistics.
GCC demography:
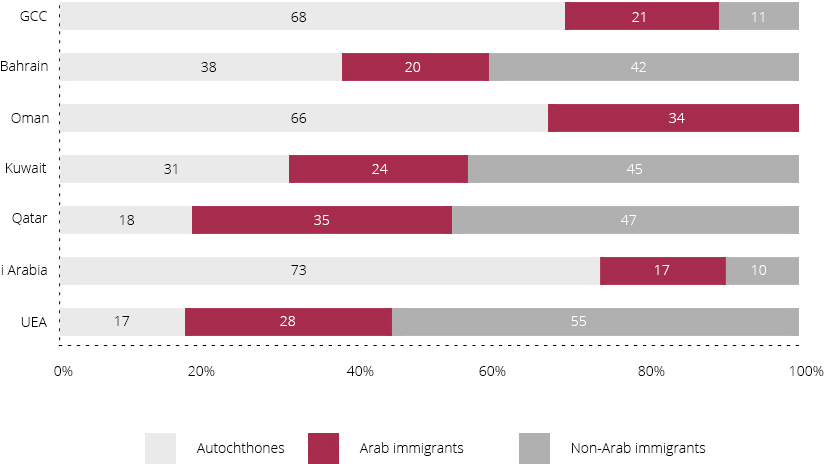
Source: IPSOS STAT